Steering System :
Steering system allows the driver to guide the moving vehicle on road and turn it right or left as he desires.
During steering, the movement of the wheel must be positive and exact and no wheel should slide on the road. This aspect is influenced by the steering linkage mechanism, tyre and road conditions and vehicle suspension system.
In order to maintain proper control throughout its speed range with safety in a straight ahead motion as well as during bumps and bounce and provide directional change with minimum effort of driver. Such mechanism is used in a vehicle is known as steering mechanism.
When a vehicle is moving on a road surface, the relative motion between the wheels and the road surface should be one of pure rolling. This condition must be satisfied when the vehicle is moving along straight or curved paths.
Steering geometry:
1.The angular relationship among the front wheels, the front wheel attaching parts and vehicle frame is known as steering geometry.
2.The various factors entering into the front end geometry and influencing the steering case/steering stability, riding quality have direct effort on tyre wear. These factors are discussed as under.
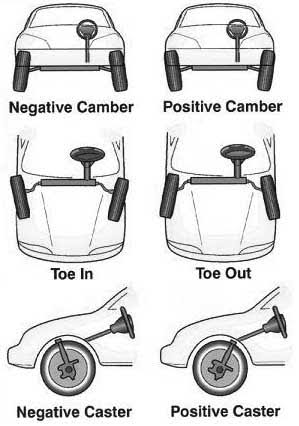
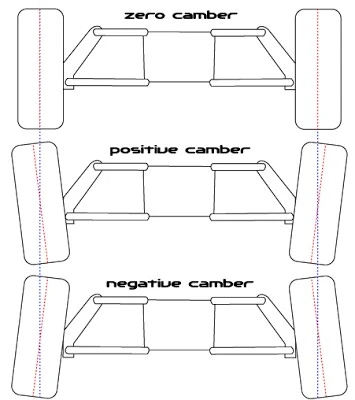
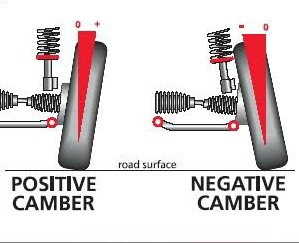
(a)Camber:
It is the angle of inclination of the front wheel tyre with respect to the vertical axis view from front of vehicle. Camber provided may be positive or negative. Camber is also called as ‘wheel rake’.
Effect :
1.When the wheel is tilted outward at the top camber is positive. Because of positive camber, the rolling radius at different points of the tyre tread is different result of which the tyre tends to roll like truncated cone about the centre of rotation, so tyre will wear more on outside.
2.Negative camber will cause the wear of tyre more on inside . Initially positive camber is provided to wheels so that when the vehicle is loaded , it automaticallycome to vertical position.
3.The tyree life will be maximum when camber camber angle is zero.
4.Amount : Camber should not be exceed 2 degrees
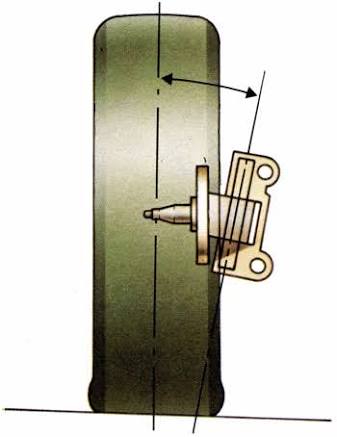
b) Kingpin inclination (Steering axis inclination) :
1.Most of the steering systems have a kingpin which is attached to steering knuckle to a support
2.In some later design kingpin is replaced by ball and socket joint. In this design, the Steering
3.knuckle and knuckle support are combined into a single part, This part is called steering knuckle. No kingpin is used in this case.
4. The steering knuckle is supported at the top and bottom by control arm,
Some Nomenclatures used generally :
1.The angle between the vertical line and centre of the kingpin or steering axle when viewed from the front of the vehicle is known as kingpin inclination or steering axis inclination.
2.The kingpin inclination ranges from 3.5 c to 8.5 0 and its average value is 5 0 . It reduces tyre wear and helps to provide steering stability. It also reduces steering effort particularly when the vehicle is stationary.
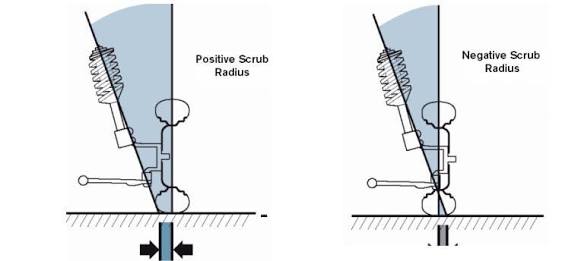
(c) Combine angle and scrub radius :
It is the angle formed in vertical plane between the wheel centre line and kingpin centre line.
Combine angle is equal to camber inclination, The angle may be to 10 The distance between the centre of the tyre patch and intersection of the kingpin or steering axis with the ground is called kingpin offset or scrub radius. Kingpin inclination or positive camber or both reduce scrub radius.
(1) If the scrub radius is negative the wheel tends to toe-in.
(2) If the scrub radius is positive the wheel tends to toe-out.
(3) If the scrub radius is zero the wheel is in straight position.
Without any tendency toe-in and toe-out : In this position the steering is called Centre point steering.
The amount of scrub radius should be upto
12 mm
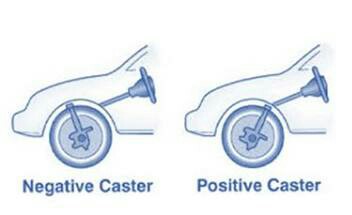
The angle between the king pin centre line and the vertical, in the plane of the wheel is called caster angle.
Caster is the slant of the steering axis as viewed from the side of the vehicle.
The steering axis is the imaginary steering pivot line which in some vehicles runs through the center of the king pin and on other runs through the canters of the upper and lower ball joint.
Caster is negative when the top of the steering axis leans to the front of the vehicle.
The steering axis intersection point is called leading point and the tyre ground contact point is called trailing point.
The positive caster is to provide directional stability. The greater the positive caster, greater is the stabilizing force. Amount of caster about 30 good result.
Toe-in is the amount by which the front wheels are set closer together at the front than at the rear when the vehicle is stationary.
Toe-out is the amount by which the wheel may be set closer at the rear than the front when the vehicle is stationary.
The difference in distance, toe-in or toe-out into a vehicle to counteract the fact that the tyres tend to change their track when the vehicle is running on the road.
An equal amount of toe-out will not cause anymore tyre wear. But this toe-out will tend to make the wheel wander and therefore toe-in is usually preferred. The correct toe-in causes rapid tyre wear, vibration and wheel wobble.
Adjustment of toe-in or toe-out is provided on all vehicle by track rod attached to the steering or on the ball joint end of the steering arms on the rack and pinion steering.
Summary:




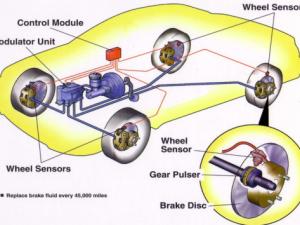 ABS known as Antilock Braking System
ABS known as Antilock Braking System